Hazardous Waste Management for Flammable Solids
Discover effective methods for the safe disposal of flammable solids with this comprehensive guide on hazardous waste management.
3 min read
 Larry Burton
:
Jun 6, 2024 10:35:00 AM
Larry Burton
:
Jun 6, 2024 10:35:00 AM
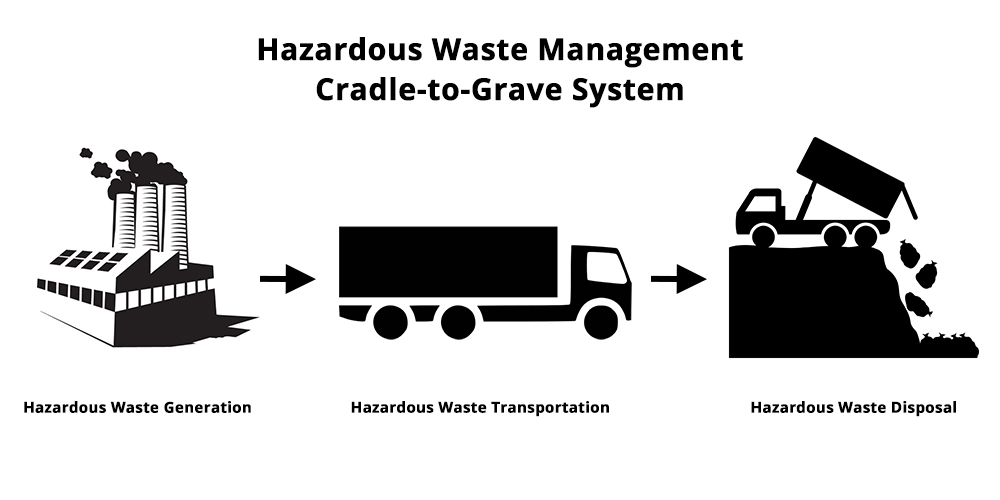
From the moment a product is conceived to its final disposal, every step in its lifecycle leaves a footprint.
This inescapable reality backs the importance of understanding the cradle to grave definition - a comprehensive approach that evaluates the environmental impact of products, materials and resources throughout their entire lifecycle.
In the context of hazardous waste management, cradle to grave concepts are especially important since your business is responsible for any waste it generates. How you treat and dispose of your waste becomes a matter of both environmental stewardship and regulatory compliance.
For manufacturing companies that generate spent solvents, meeting the cradle to grave definition offers an opportunity to not only ensure compliance, but also improve the sustainability of your operations by taking advantage of advanced technology that produces high recovery volumes.
Cradle to grave is a comprehensive approach used to evaluate the environmental impact of a product, material or substance from its inception (cradle) to its ultimate disposal (grave).
substance from its inception (cradle) to its ultimate disposal (grave).
This concept encompasses all stages of a product’s lifecycle, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, distribution, use and disposal.
The cradle-to-grave framework considers the environmental inputs and outputs associated with each stage of a product's lifecycle, including energy consumption, resource depletion, emissions and waste generation. Analyzing the entire lifecycle, from production to disposal, cradle to grave, provides valuable insights into the environmental footprint of products and materials, helping to identify opportunities for improvement and sustainable practices.
This approach is widely used in various industries, from manufacturing to construction and hazardous waste management. Particularly with hazardous waste management, cradle to grave emphasizes that from the moment waste is generated until its final disposal, you are accountable for its environmental impact.
In manufacturing, the cradle-to-grave approach holds significant importance, especially for companies that generate spent solvents and industrial chemicals. Although these substances are integral to many manufacturing processes, they also pose environmental and health risks if not handled responsibly throughout their lifecycle.
The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) gives the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency the authority to control hazardous waste from cradle to grave. This includes the generation, transportation, treatment, storage and disposal of all hazardous wastes.
In industry, some commonly used solvents include:
Some spent solvents can contain toxic or carcinogenic compounds that pose significant risks to ecosystems and human health if improperly managed. By implementing cradle-to-grave principles, you can ensure that hazardous materials are handled in a manner that minimizes environmental impact and complies with regulatory requirements.
Cradle-to-grave practices can even yield economic benefits for your manufacturing company. By optimizing resource use, reducing waste generation and mitigating environmental risks, you can enhance operational efficiency, minimize costs associated with waste management, and bolster your reputation as an environmentally responsible entity.
When halogenated and non-halogenated solvents like the ones listed above are distilled and recycled, your business can contribute to reducing the amount of virgin raw materials that are purchased.
What is solvent distillation? Solvent distillation involves taking a liquid or vapor mixture of two or more substances and separating it into its component fractions of desired purity.
This process separates the solvents from other substances through the application of heat. The basic principle is to heat a liquid mixture containing solvents, causing the solvent to vaporize. The vapor is then condensed back into a liquid form, resulting in the separation and recovery of the solvent.
When choosing a solvent distillation plant to handle your hazardous waste, it’s important to choose one that uses energy-efficient technology and achieves high recovery volume to gain the highest level of sustainability.
At Samex, our solvent recycling process reduces volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions while repurposing any waste water that is processed. Nothing gets sent to landfills.
Other indicators that you have chosen a high-quality plant that focuses on sustainable operations include:
At Samex, we send any distillation bottoms to the alternative fuel formulation section of the plant where they are blended and repurposed. Distillation bottoms include sediments and other matters separated from the solvent during this process.
Check to make sure that when the solvent distillation company or service provider is transporting your waste to the plant, it follows all safety regulations. Transportation of your waste is part of the cradle to grave process, so it’s critical to prioritize preventing any risks that come with this part of the disposal plan.
A solvent distillation plant or service provider with a strong focus on waste transporter safety will have:
While a solvent distillation plant can help you achieve high levels of sustainability, it’s also important to select one that prioritizes safety on the road and sustainable operations at the plant. Energy-efficient technology, high recovery volumes and a focus on minimizing emissions and waste are all clues that the plant you are partnering with is as committed to environmental responsibility and resource efficiency as your manufacturing business.

Discover effective methods for the safe disposal of flammable solids with this comprehensive guide on hazardous waste management.

Discover the essential regulations and guidelines for the safe disposal of flammable liquid waste. Understand the importance of proper handling and...

In manufacturing, efficiency isn’t just about maximizing production. It’s also about minimizing waste.