Your Guide To Flammability Class Awareness And Disposal
In industrial operations, a silent but significant risk looms large: flammable materials.

As a hazardous waste generator, you are responsible for any waste you produce during its ENTIRE lifestyle.
Known as “cradle to grave,” this requirement is heavily enforced at both state and federal levels, and places the responsibility on your business to ensure any hazardous waste you generate is safely disposed of according to the law.
Taking short cuts, neglecting proper procedures or failing to comply will lead to severe problems that are far worse and far more challenging than taking the proper steps to follow these hazardous waste regulations.
While most businesses realize they must manage their waste when it’s onsite, they run into problems during transportation and final disposal. You may believe that when you hand your waste off to another party, the waste becomes that other company’s responsibility. However, cradle to grave laws do not absolve you of your duty in making sure your waste is properly disposed of.
That leaves you with the pressing question: How can you minimize your company’s potential liability once the hazardous waste is out of your hands?
Here are some frequently asked questions about cradle to grave requirements and the important information about why the disposal process you choose for your waste can have a significant impact on your cradle to grave responsibilities.
Cradle to grave is a term that describes the comprehensive responsibility a business has for the entire lifecycle of hazardous waste it generates. This concept mandates that businesses are accountable for their hazardous waste from the point of generation (the “cradle”) through its transportation, treatment, storage and ultimate disposal (the “grave”).
Compliance with cradle to grave regulations ensures that hazardous waste is managed safely and in accordance with all applicable laws to protect human health and the environment.
The “cradle to grave” responsibility for hazardous waste originates from the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) of 1976. The RCRA is a federal law in the United States enacted to address the growing problem of municipal and industrial waste. It provides the framework for the proper management of hazardous and non-hazardous solid waste.
Under the RCRA, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is authorized to control hazardous waste from its creation to its disposal, encompassing generation, transportation, treatment, storage and disposal.
The RCRA also includes provisions for managing non-hazardous solid waste and establishes a system for managing hazardous waste from “cradle to grave.” This law forms the basis for the stringent regulatory framework that governs hazardous waste management in the United States.
Penalties for non-compliance with cradle to grave regulations under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) can be severe. Businesses can face substantial civil fines, reaching into the thousands per day for each violation.
Serious violations may result in criminal charges and even imprisonment. Regulatory authorities can also seek injunctions to compel compliance, which may require businesses to cease operations until violations are addressed. Businesses may be held financially responsible for cleanup costs and natural resource damages resulting from improper hazardous waste management as well.
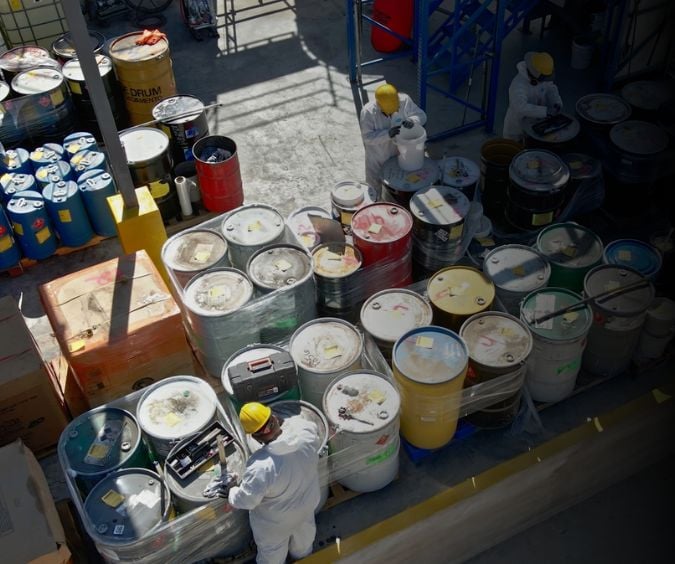
A hazardous waste transport company must be licensed and offer comprehensive transportation services to ensure safe and legal handling of hazardous materials. This includes proper labeling, packaging and documentation of hazardous waste to meet all regulatory requirements.
Some treatment, storage and disposal facilities (TSDFs) will transport waste from your worksite as well. If a TSDF transports waste, it should have a fleet of vehicles and trucks that incorporate secure elements that include:
Selecting a plant with a strong focus on transportation safety is crucial for ensuring a comprehensive and responsible waste management approach that extends beyond the plant to the entire waste journey.
This disposal process you choose for your waste can also have a significant impact on your cradle to grave responsibilities.

For example, if you transport your waste to Mexico, your cradle to grave liability ends at the U.S-Mexico border. For generators located in the Southwest United States, that shorter transport distance can provide some relief in terms of logistical costs, while lessening your concern about extended liability for your waste management responsibilities.
But is exporting hazardous waste safe? Yes, as long as you work with a reputable and licensed transporter or treatment facility.
Samex Environmental Services has all the authorizations needed for the export of hazardous waste to Mexico, where we operate state-of-the-art solvent distillation and waste to energy technologies in Tijuana. TSDFs and hazardous waste transporters must meet both U.S. and Mexico standards and are subject to regular inspections by Mexican regulatory agencies, including the equivalent to the United States EPA and OSHA.
Once your waste arrives at the border, Samex assumes liability at that point. Here’s a step-by-step look at how our export process works:
If it was not legal for Samex to export hazardous waste shipments, the EPA would not grant authorization for the transfer to take place.
Transporting your waste to Mexico can also provide additional benefits if your business generates hazardous waste like spent solvents, flammable liquids and flammable solids. At Samex, nothing is wasted during the solvent distillation process, so your company can enjoy a boost in its sustainability for the management of your hazardous waste. Southwest U.S. companies may also see lower transportation costs and a reduced carbon footprint by using less fuel for transport.
In the end, one of the greatest benefits is that Samex becomes the principal party for your waste at the border, reducing your cradle to grave liability. In today’s highly regulatory environment, every step you take to enhance sustainability and reduce liability demonstrates your commitment to securing a cleaner environmental impact and a protected future for your company.

In industrial operations, a silent but significant risk looms large: flammable materials.

The proper storage of flammable liquids stands as a critical line of defense against potential disasters.
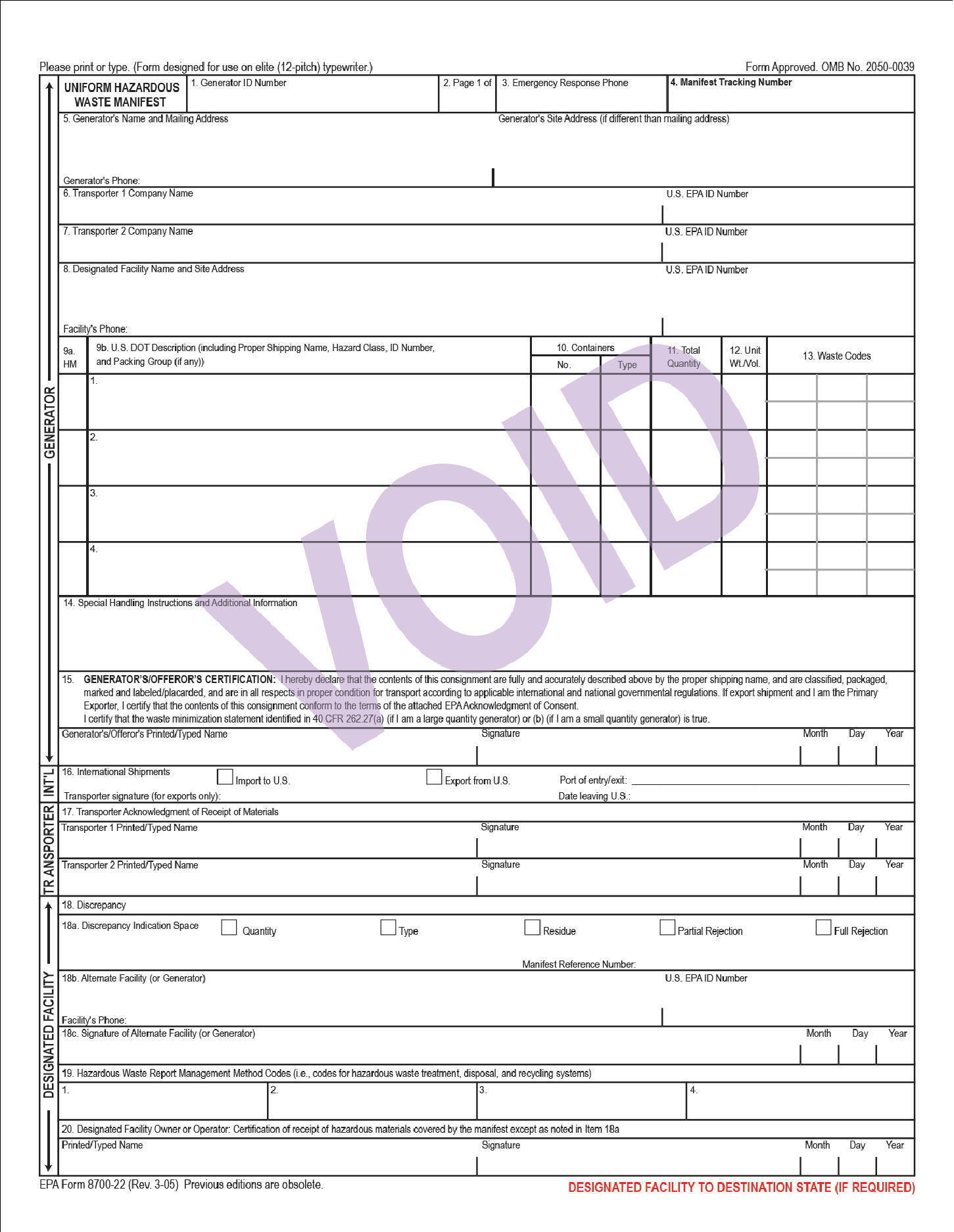
If your company generates hazardous waste and ships that waste to a facility in the United States, you’re no stranger to the biennial report—it rolls...